Kolekce Free Radical Atom
Kolekce Free Radical Atom. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.
Prezentováno Free Radical Bioscience Notes
Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism.
Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive... A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron.

A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism.

Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions.

Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive.. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).

Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).

The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism.

A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions... Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons... Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical... Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.

Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical )... A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron.
/freeradical-5c59e9bdc9e77c000159b251.jpg)
An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive.. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical.

An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical.

Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule... Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron.

Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.
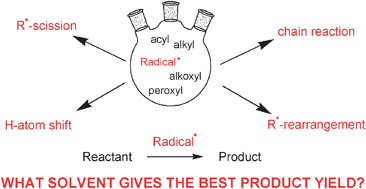
Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. .. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical.

Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.

Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence... An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the.

Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical... Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence... A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism.
Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism.

An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the... Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism... Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions.

Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron.

Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical.. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).

Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron.. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the.

An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the... Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals... Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron.

Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule... The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the.
They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. . Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals.

Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.
Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.
The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive.
The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive... .. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical.. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron.. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).

Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron.. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the.

Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism... An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions... Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Free radical formation occurs continuously in the cells as a consequence of both enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.

An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ).. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.

The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive... . An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the.

Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the... Jan 21, 2010 · definition and structure of free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Jul 15, 2014 · free radicals are the products of normal cellular metabolism. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and highly reactive.. A free radical can be defined as an atom or molecule containing one or more unpaired electrons in valency shell or outer orbit and is capable of independent existence.

Instead, a radical, specifically a free radical, is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Needless t electrons are not always paired, however, even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical (or simply a radical ). Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells. Hydrogen atom as the smallest free radical. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to dna and other parts of human cells.
